CardioLyfe offers advanced cardiac care with modern facilities and expert guidance from a renowned heart specialist, ensuring precision, safety, and faster recovery.
Get 24/7 emergency heart care at CardioLyfe. Leading cardiac experts ensure rapid response and life-saving treatment for heart attacks, arrhythmias, and critical heart conditions.
With 20+ years in cardiology, the interventional cardiologist is trusted for complex angioplasty, stenting, and pacemaker procedures with high success rates across India.
At CardioLyfe, a globally acclaimed team of heart surgeons, cardiologists work effectively to provide comprehensive care for various heart ailments.

Our globally recognized team of expert cardiologists and heart surgeons, led by the Top Heart Doctor Shalimar Bagh, specializes in providing advanced cardiac care for a wide range of heart diseases. Using state-of-the-art technology and evidence-based treatment protocols, we ensure the highest standards of heart health and patient care.
Dr. Sudhanshu Sekhar Parida is a highly respected and accomplished heart specialist, renowned as a gold medallist in MBBS, MD Medicine (AIIMS), and DM Cardiology (GB Pant), with prestigious fellowships including FACC, FSCAI, and FESC.
Recognized as one of the best interventional cardiologists in Shalimar Bagh, Delhi, Dr. Parida has earned national trust with a 99% success rate in advanced cardiac procedures. His dedication and long-term success in treating hundreds of heart patients make him a preferred choice for those seeking expert and minimally invasive heart care.
At CardioLyfe, a globally renowned cardiac center, Dr. Parida works with an elite team of cardiologists and heart specialists to deliver advanced and compassionate care for a wide range of cardiovascular conditions.
✅ Led by the Best: Headed by Dr. Sudhansu Sekhar Parida, a highly experienced and trusted Interventional Cardiologist in Shalimar Bagh, Delhi, known for delivering top-tier cardiac care.
✅ Patient-Centric Approach: Every treatment plan is uniquely designed, focusing on individual health needs and ensuring complete transparency and trust in every interaction.
✅ Advanced Cardiac Procedures: Expertise in transradial angiography, TAVI, MICRA implantation, and structural heart interventions ensures that patients receive the latest and safest heart treatments.
✅ 24/7 Support & Care: Our team of cardiologists and trained paramedics ensures continuous care, from diagnosis to post-procedure follow-up.
✅ State-of-the-Art Facility: Equipped with the latest intravascular imaging tools (OCT, IVUS) and technologies for accurate, minimally invasive procedures.
✅ Ethical & Empathetic Care: We prioritize empathy, ethics, and excellence, treating every patient with dignity, respect, and 100% commitment.
✅ Trusted by Thousands: Backed by 30,000+ successful procedures, Dr. Parida has earned a reputation for clinical precision and compassionate care.
We are always ready to serve with compassion. Throughout your health recovery journey, we ensure access to the most advanced medical facilities and personalized care. Our commitment lies in delivering patient-centered care, forming trusted partnerships that lead to better health outcomes and a more fulfilling life.
Our highly experienced and qualified cardiology team can effectively treat all heart diseases and do all cardiac interventions. We Offer Different Services To Improve Your Health
Coronary angiography is a medical procedure used to visualize the blood vessels in the heart, particularly the coronary arteries. It helps to identify blockages or narrowing in the coronary arteries that may be restricting blood flow to the heart muscle.
Service Details →It is a minimally invasive procedure used to widen narrowed or blocked coronary arteries to improve blood flow to the heart muscle. Coronary angioplasty is commonly used to treat conditions such as coronary artery disease (CAD).
Service Details →A pacemaker is a device that sends small electrical impulses to the heart muscle to maintain a suitable heart rate. An area below the collar bone will be numbed with local anesthetic and the cardiologist will make a small cut (approx. 5-8cms) to insert the pacemaker.
Service Details →It is an electronic device that constantly monitors your heart rhythm. When it detects a very fast, abnormal heart rhythm, it delivers energy to the heart muscle.
Service Details →Congestive heart failure is quite common nowdays. The probability of people in this category is relatively high. The heart is a muscular valve that pumps blood to various regions of the body. Heart failure occurs when the heart's pump gets weak and the heart is unable to pump the amount of blood that the body requires.
Service Details →Rota ablation is a procedure during angioplasty in which a tiny drill with a diamond-tipped burr, powered by compressed air to break up calcified plaque (hard block) that is clogging the coronary artery. Breaking up the plaque restores blood flow to the heart.
Service Details →The Department of Cardiology at Fortis Hospital Shalimar Bagh New Delhi been providing cardiac care for more than two decades. It was shifted to superspeciality block in 2015. It has developed world class cardiology centre with cardiac care facility comparable to any advanced cardiology centre in the world.
To Learn More Check Out Our Success Stories
Many thanks to Dr Sudhanshu Sekhar Parida. Great experience as a first timer. I especially loved how Doc really took his time to explain my conditions with me as well as my treatment option.

Happy with Explanation of the health issue Need time for more response but still I am satisfied for currently sitting and situation of my problem.

A great doctor who easily diagnosed the issue and explained it so easily in layman language. Gave a step by step procedure for treatment which was extremely helpful. Thankyou for your help!

Dr. Sudhanshu Sekhar Parida is a cardiologist with over 20 years of expertise who can perform complex angioplasty, stenting, pacemaker and device implantations. The National Board of Examinations in New Delhi awarded him a Post-Doctoral Fellowship in Interventional Cardiology.

Keep Up With Our Most Recent Cardiology Articles & News

Discover the top exercises recommended by cardiologists to strengthen your heart, reduce the risk of heart disease, and improve overall wellness. Learn simple and safe workouts for a healthy lifestyle.
Details →
Discover the top exercises recommended by cardiologists to strengthen your heart, reduce the risk of heart disease, and improve overall wellness. Learn simple and safe workouts for a healthy lifestyle.
Details →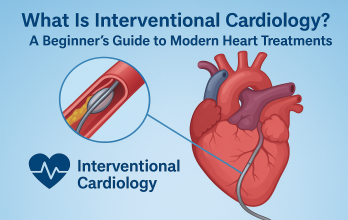
Interventional cardiology is a modern branch of heart care that uses minimally invasive, catheter-based procedures like angioplasty and stenting to treat blocked arteries, heart valve disorders, and other cardiac conditions—helping patients recover faster with reduced risks.
Details →
Looking for the best cardiologist near Shalimar Bagh? This guide helps you make an informed decision with tips on experience, certifications, facilities, and patient reviews.
Details →Join our community and receive expert insights, the latest heart health tips, and updates directly from leading cardiologists. Whether you're looking to maintain a healthy heart or manage existing conditions, our newsletter is your go-to resource for all things cardiovascular.